interview
并发篇
1. 线程状态
要求
- 掌握 Java 线程六种状态
- 掌握 Java 线程状态转换
- 能理解五种状态与六种状态两种说法的区别
六种状态及转换
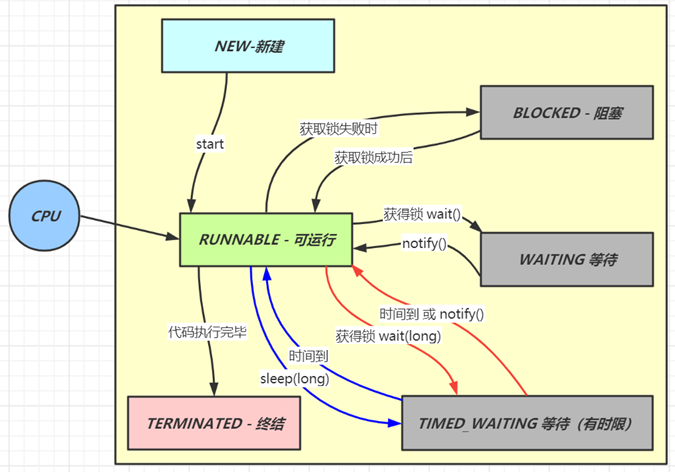
分别是
- 新建
- 当一个线程对象被创建,但还未调用 start 方法时处于新建状态
- 此时未与操作系统底层线程关联
- 可运行
- 调用了 start 方法,就会由新建进入可运行
- 此时与底层线程关联,由操作系统调度执行
- 终结
- 线程内代码已经执行完毕,由可运行进入终结
- 此时会取消与底层线程关联
- 阻塞
- 当获取锁失败后,由可运行进入 Monitor 的阻塞队列阻塞,此时不占用 cpu 时间
- 当持锁线程释放锁时,会按照一定规则唤醒阻塞队列中的阻塞线程,唤醒后的线程进入可运行状态
- 等待
- 当获取锁成功后,但由于条件不满足,调用了 wait() 方法,此时从可运行状态释放锁进入 Monitor 等待集合等待,同样不占用 cpu 时间
- 当其它持锁线程调用 notify() 或 notifyAll() 方法,会按照一定规则唤醒等待集合中的等待线程,恢复为可运行状态
- 有时限等待
- 当获取锁成功后,但由于条件不满足,调用了 wait(long) 方法,此时从可运行状态释放锁进入 Monitor 等待集合进行有时限等待,同样不占用 cpu 时间
- 当其它持锁线程调用 notify() 或 notifyAll() 方法,会按照一定规则唤醒等待集合中的有时限等待线程,恢复为可运行状态,并重新去竞争锁
- 如果等待超时,也会从有时限等待状态恢复为可运行状态,并重新去竞争锁
- 还有一种情况是调用 sleep(long) 方法也会从可运行状态进入有时限等待状态,但与 Monitor(监视器) 无关,不需要主动唤醒,超时时间到自然恢复为可运行状态
- wating等待,执行notify后要去争抢锁,拿到锁后进入可运行状态,否则阻塞线程。
- sleep睡眠时间到了直接进入可运行状态,不需要争抢锁
其它情况(只需了解)
- 可以用 interrupt() 方法打断等待、有时限等待的线程,让它们恢复为可运行状态
- park,unpark 等方法也可以让线程等待和唤醒
五种状态
五种状态的说法来自于操作系统层面的划分
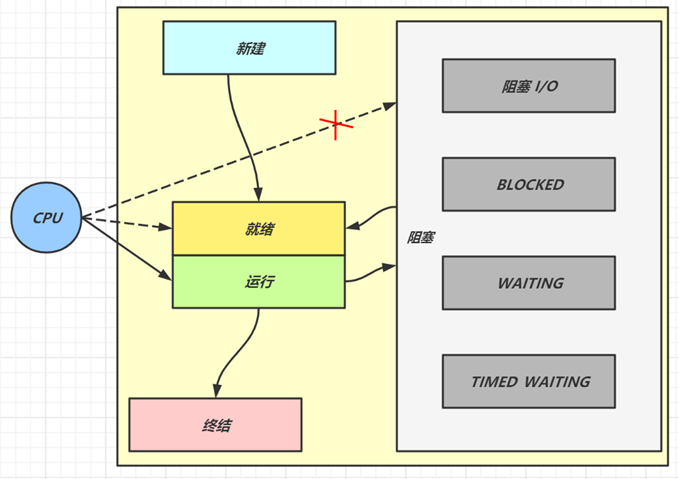
- 运行态:分到 cpu 时间,能真正执行线程内代码的
- 就绪态:有资格分到 cpu 时间,但还未轮到它的
- 阻塞态:没资格分到 cpu 时间的
- 涵盖了 java 状态中提到的阻塞、等待、有时限等待
- 多出了阻塞 I/O,指线程在调用阻塞 I/O 时,实际活由 I/O 设备完成,此时线程无事可做,只能干等
- 新建与终结态:与 java 中同名状态类似,不再啰嗦
2. 线程池
要求
- 掌握线程池的 7 大核心参数
七大参数
- corePoolSize 核心线程数目 - 池中会保留的最多线程数
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目 - 核心线程+救急线程的最大数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 救急线程的生存时间,生存时间内没有新任务,此线程资源会释放
- unit 时间单位 - 救急线程的生存时间单位,如秒、毫秒等
- workQueue - 当没有空闲核心线程时,新来任务会加入到此队列排队,队列满会创建救急线程执行任务
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以定制线程对象的创建,例如设置线程名字、是否是守护线程等
- handler 拒绝策略 - 当所有线程都在繁忙,workQueue 也放满时,会触发拒绝策略
- 抛异常 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
- 由调用者执行任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy
- 丢弃任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy
- 丢弃最早排队任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy
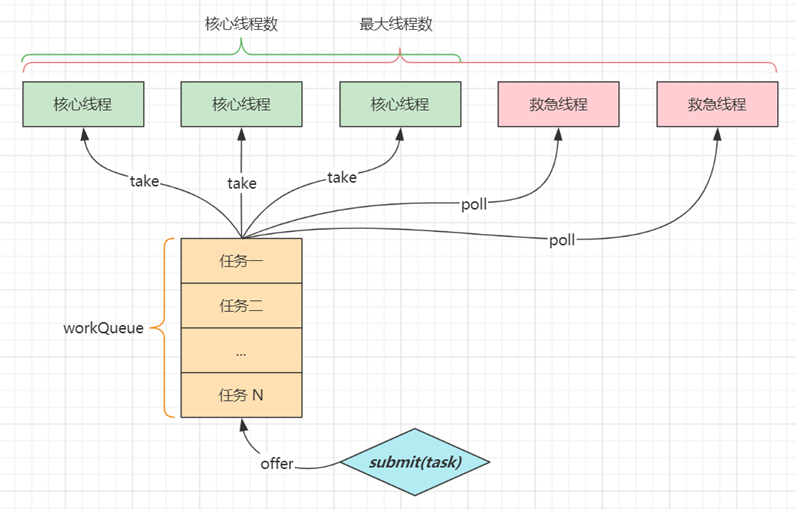
代码说明
day02.TestThreadPoolExecutor 以较为形象的方式演示了线程池的核心组成
3. wait vs sleep
要求
- 能够说出二者区别
一个共同点,三个不同点
共同点
- wait() ,wait(long) 和 sleep(long) 的效果都是让当前线程暂时放弃 CPU 的使用权,进入阻塞状态
不同点
- 方法归属不同
- sleep(long) 是 Thread 的静态方法
- 而 wait(),wait(long) 都是 Object 的成员方法,每个对象都有
- 醒来时机不同
- 执行 sleep(long) 和 wait(long) 的线程都会在等待相应毫秒后醒来
- wait(long) 和 wait() 还可以被 notify 唤醒,wait() 如果不唤醒就一直等下去
- 它们都可以被打断唤醒
- 锁特性不同(重点)
- wait 方法的调用必须先获取 wait 对象的锁,而 sleep 则无此限制
- wait 方法执行后会释放对象锁,允许其它线程获得该对象锁(我放弃 cpu,但你们还可以用)
- 而 sleep 如果在 synchronized 代码块中执行,并不会释放对象锁(我放弃 cpu,你们也用不了)
4. lock vs synchronized
要求
- 掌握 lock 与 synchronized 的区别
- 理解 ReentrantLock 的公平、非公平锁
- 理解 ReentrantLock 中的条件变量
三个层面
不同点
- 语法层面
- synchronized 是关键字,源码在 jvm 中,用 c++ 语言实现
- Lock 是接口,源码由 jdk 提供,用 java 语言实现
- 使用 synchronized 时,退出同步代码块锁会自动释放,而使用 Lock 时,需要手动调用 unlock 方法释放锁
- 功能层面
- 二者均属于悲观锁、都具备基本的互斥、同步、锁重入功能
- Lock 提供了许多 synchronized 不具备的功能,例如获取等待状态、公平锁、可打断、可超时、多条件变量
- Lock 有适合不同场景的实现,如 ReentrantLock, ReentrantReadWriteLock
- 性能层面
- 在没有竞争时,synchronized 做了很多优化,如偏向锁、轻量级锁,性能不赖
- 在竞争激烈时,Lock 的实现通常会提供更好的性能
公平锁
- 公平锁的公平体现
- 已经处在阻塞队列中的线程(不考虑超时)始终都是公平的,先进先出
- 公平锁是指未处于阻塞队列中的线程来争抢锁,如果队列不为空,则老实到队尾等待
- 非公平锁是指未处于阻塞队列中的线程来争抢锁,与队列头唤醒的线程去竞争,谁抢到算谁的
- 公平锁会降低吞吐量,一般不用
ReentrantLock可重入锁
- ReentrantLock 中的条件变量功能类似于普通 synchronized 的 wait,notify,用在当线程获得锁后,发现条件不满足时,临时等待的链表结构
- 与 synchronized 的等待集合不同之处在于,ReentrantLock 中的条件变量可以有多个,可以实现更精细的等待、唤醒控制
- getOwner() 线程持有者
- getState()=0 未加锁 如果加锁state加一
- tryLock尝试获得锁,超时获取不到锁返回false,线程不会进入阻塞队列。
- blocked queue阻塞队列是双向链表
- 条件变量(队列)newCondition 对象await方法进入等待队列
条件变量
- 如果是构造非公平 可重入对象时,tryLock会跟阻塞队列中的线程争抢锁否则不会争抢锁。
- 无参数tryLock不区分用的是非公平锁
- signal()方法唤醒,如果获取不到锁将重新进入阻塞队列。
- waiting queue是单向链表(可重入锁对象.newCondition().awat();)
代码说明
- day02.TestReentrantLock 用较为形象的方式演示 ReentrantLock 的内部结构
5. volatile
要求
- 掌握线程安全要考虑的三个问题
- 掌握 volatile 能解决哪些问题
原子性
- 起因:多线程下,不同线程的指令发生了交错导致的共享变量的读写混乱
- 解决:用悲观锁或乐观锁解决,volatile 并不能解决原子性
可见性
- 起因:由于编译器优化、或缓存优化、或 CPU 指令重排序优化导致的对共享变量所做的修改另外的线程看不到
- 解决:用 volatile 修饰共享变量,能够防止编译器等优化发生,让一个线程对共享变量的修改对另一个线程可见
- jit热点代码优化(-Xint(jvm参数)不使用jit进行解释10倍到100倍)
- 循环超过阈值时,会优化代码进行编译,之后不再从内存中读取源码编译。
- volatile不优化相差10倍循环次数
有序性
- 起因:由于编译器优化、或缓存优化、或 CPU 指令重排序优化导致指令的实际执行顺序与编写顺序不一致
- 解决:用 volatile 修饰共享变量会在读、写共享变量时加入不同的屏障,阻止其他读写操作越过屏障,从而达到阻止重排序的效果
- 注意:
- volatile 变量写加的屏障是阻止上方其它写操作越过屏障排到 volatile 变量写之下
- volatile 变量读加的屏障是阻止下方其它读操作越过屏障排到 volatile 变量读之上
- volatile 读写加入的屏障只能防止同一线程内的指令重排
代码说明
- day02.threadsafe.AddAndSubtract 演示原子性
- day02.threadsafe.ForeverLoop 演示可见性
- 注意:本例经实践检验是编译器优化导致的可见性问题
- day02.threadsafe.Reordering 演示有序性
- 需要打成 jar 包后测试
- 请同时参考视频讲解
- 对于写操作不能越过屏障重新排序到下面,可以先执行屏障下面的指令
- 写入用volatite修饰的变量时应该放下面
- 读操作不能往上读(返过来)
6. 悲观锁 vs 乐观锁
要求
- 掌握悲观锁和乐观锁的区别
对比悲观锁与乐观锁
- 悲观锁的代表是 synchronized 和 Lock 锁
- 其核心思想是【线程只有占有了锁,才能去操作共享变量,每次只有一个线程占锁成功,获取锁失败的线程,都得停下来等待】
- 线程从运行到阻塞、再从阻塞到唤醒,涉及线程上下文切换,如果频繁发生,影响性能
- 实际上,线程在获取 synchronized 和 Lock 锁时,如果锁已被占用,都会做几次重试操作,减少阻塞的机会
- 乐观锁的代表是 AtomicInteger,使用 cas 来保证原子性(底层是UnSafe 通常会将变量修饰为volatile来实现乐观锁)
- 其核心思想是【无需加锁,每次只有一个线程能成功修改共享变量,其它失败的线程不需要停止,不断重试直至成功】
- 由于线程一直运行,不需要阻塞,因此不涉及线程上下文切换
- 它需要多核 cpu 支持,且线程数不应超过 cpu 核数 ```java // 在JDK9之后,sun.misc.Unsafe被移动到jdk.unsupported模块中,同时在java.base模块克隆了一个jdk.internal.misc.Unsafe类 // 代替了JDK8以前的sun.misc.Unsafe的功能,jdk.internal包不开放给开发者调用。 //import jdk.internal.misc.Unsafe; //jdk8 import sun.misc.Unsafe;
// –add-opens java.base/jdk.internal.misc=ALL-UNNAMED public class SyncVsCas { static final Unsafe UNSAFE_9 = Unsafe.getUnsafe(); // CAS 操作需要知道要操作的字段的内存地址 static final long BALANCE = UNSAFE_9.objectFieldOffset(Account.class, “balance”); // 在指定的类中查找指定的字段,并返回该字段在内存中的偏移量 Unsafe.getUnsafe().objectFieldOffset(Account.class, “balance”)
static class Account { // 进行 CAS 操作时通常需要加 volatile 修饰变量,保证该字段的可见性和有序性。 volatile int balance = 10; // 余额 }
private static void showResult(Account account, Thread t1, Thread t2) { try { t1.start(); t2.start(); t1.join(); t2.join(); LoggerUtils.get().debug(“{}”, account.balance); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
public static void sync(Account account) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (account) { int old = account.balance; int n = old - 5; account.balance = n; } },”t1”);
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (account) {
int o = account.balance;
int n = o + 5;
account.balance = n;
}
},"t2");
showResult(account, t1, t2); }
public static void cas(Account account) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { // 乐观锁 while (true) { int o = account.balance; int n = o - 5; // 比较和设置CAS if (UNSAFE_9.compareAndSetInt(account, BALANCE, o, n)) { break; } } },”t1”);
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
int o = account.balance;
int n = o + 5;
if (UNSAFE_9.compareAndSetInt(account, BALANCE, o, n)) {
break;
}
}
},"t2");
showResult(account, t1, t2); }
private static void basicCas(Account account) { while (true) { int o = account.balance; int n = o + 5; if(UNSAFE_9.compareAndSetInt(account, BALANCE, o, n)){ break; } } System.out.println(account.balance); }
public static void main(String[] args) { Account account = new Account(); cas(account); } }
该方法会比较 expectedValue 和当前引用所指向的值,如果相同,则将该引用设置为 newValue。
```java
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class OptimisticLock {
private AtomicReference<Object> value = new AtomicReference<>(new Object());
public Object getValue() {
return value.get();
}
public boolean update(Object expectedValue, Object newValue) {
return value.compareAndSet(expectedValue, newValue);
}
}
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
// -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=24m
// 模拟不断生成类, 但类无法卸载的情况
public class TestOomTooManyClass {
// static GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell();
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
while (true) {
try (FileReader reader = new FileReader("script")) {
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell();
shell.evaluate(reader);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.incrementAndGet());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
monitor监控(线程阻塞状态)
代码说明
- day02.SyncVsCas 演示了分别使用乐观锁和悲观锁解决原子赋值
- 请同时参考视频讲解
7. Hashtable vs ConcurrentHashMap
要求
- 掌握 Hashtable 与 ConcurrentHashMap 的区别
- 掌握 ConcurrentHashMap 在不同版本的实现区别
更形象的演示,见资料中的 hash-demo.jar,运行需要 jdk14 以上环境,进入 jar 包目录,执行下面命令
java -jar --add-exports java.base/jdk.internal.misc=ALL-UNNAMED hash-demo.jar
Hashtable 对比 ConcurrentHashMap
- Hashtable 与 ConcurrentHashMap 都是线程安全的 Map 集合
- Hashtable 并发度低,整个 Hashtable 对应一把锁,同一时刻,只能有一个线程操作它
- Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
- hash & 0x7FFFFFF哈希按位与最大正数得到正数,再进行% tab.length取模数组容量得到索引
- 默认情况下,它的容量为 11,超过0.75时,扩容为2n+1。
- ConcurrentHashMap 并发度高,整个 ConcurrentHashMap 对应多把锁,只要线程访问的是不同锁,那么不会冲突
ConcurrentHashMap 1.7
ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel)
-
默认的构造函数,默认的扩容因子是0.75,容量是16.
- 数据结构:
Segment(大数组) + HashEntry(小数组) + 链表,每个 Segment 对应一把锁,如果多个线程访问不同的 Segment,则不会冲突 - 并发度:Segment 数组大小即并发度,决定了同一时刻最多能有多少个线程并发访问。Segment 数组不能扩容,意味着并发度在 ConcurrentHashMap 创建时就固定了
- 索引计算
- Segment数组的长度是2的整数次幂。 $2^m$,key 在大数组内的索引是 key 的二次 hash 值的高 m 位
- 小数组长度是 $2^n$,key 在小数组内的索引是 key 的二次 hash 值的低 n 位
- 扩容:每个小数组的扩容相对独立,小数组在超过扩容因子时会触发扩容,每次扩容翻倍
- Segment[0] 原型:首次创建其它小数组时,会以此原型为依据,数组长度会以原型为准
ConcurrentHashMap 1.8
- 数据结构:
Node 数组 + 链表或红黑树,数组的每个头节点作为锁,如果多个线程访问的头节点不同,则不会冲突。首次生成头节点时如果发生竞争,利用 cas(Compare-and-Swap)而非 syncronized,进一步提升性能。 - 如果在ConcurrentHashMap中发生并发,它会采用分段锁机制来解决。ConcurrentHashMap将整个哈希表分成多个桶,对每个桶使用独立的锁进行保护,这样就可以有效地减小锁的粒度,提高并发性能。
- 这样的做法可以让大多数读操作在不加锁的情况下并发进行,只有当读操作和写操作同时发生在同一个桶上时才会进行锁竞争。因此,可以在保证数据的完整性的同时,大大提高了读写并发性能。
- ConcurrentHashMap使用的锁是基于Java中的ReentrantLock(重入锁)实现的。ReentrantLock是一种可重入的互斥锁,允许在同一线程中多次获取锁,而不会导致死锁。这对于ConcurrentHashMap来说非常有用,因为在分段锁机制中,某一个线程可能会在不同的桶上获取锁。
- ReentrantLock支持两种获取锁的方式:非公平锁和公平锁。ConcurrentHashMap默认采用非公平锁,意味着锁竞争时获取锁的顺序不一定是按照请求锁的顺序进行的。
- 在ConcurrentHashMap中,每个桶都是一个链表,其中存储了所有具有相同哈希值的键值对。当线程试图对哈希表进行写操作时,它会先获取桶所对应的锁,然后再进行操作。
- 分段锁机制可以保证读操作在不加锁的情况下并发进行,只有当读操作和写操作同时发生在同一个桶上时才会进行锁竞争。 *
- 并发度:Node 数组有多大,并发度就有多大,与 1.7 不同,Node 数组可以扩容
- 扩容条件:Node 数组满 3/4 时就会扩容
- 扩容单位:以链表为单位从后向前迁移链表,迁移完成的将旧数组头节点替换为 ForwardingNode(转发节点)
- 扩容时并发 get
- 根据是否为 ForwardingNode 来决定是在新数组查找还是在旧数组查找,不会阻塞
- 如果链表长度超过 1,则需要对节点进行复制(创建新节点),怕的是节点迁移后 next 指针改变
- 如果链表最后几个元素扩容后索引不变,则节点无需复制
- 扩容时并发 put
- 如果 put 的线程与扩容线程操作的链表是同一个,put 线程会阻塞
- 如果 put 的线程操作的链表还未迁移完成,即头节点不是 ForwardingNode,则可以并发执行
- 如果 put 的线程操作的链表已经迁移完成,即头结点是 ForwardingNode,则可以协助扩容
- 与 1.7 相比是懒惰初始化
- capacity 代表预估的元素个数,capacity / factory 来计算出初始数组大小,需要贴近 $2^n$
- loadFactor 只在计算初始数组大小时被使用,之后扩容固定为 3/4
- 超过树化阈值时的扩容问题,如果容量已经是 64,直接树化,否则在原来容量基础上做 3 轮扩容 *
- ConcurrentHashMap7是饿汉式初始化
- 构造函数3个参数:容量,扩容因子,并发度
- 原型数组segment[0]:容量除于并发度等于小数组(hashEntry),最小等于2(饿汉式),
- 在其他segment[n]创建时使用原型的容量
- 索引:容量2的n次幂 需要二次哈希,移位 按位与(取二次哈希二进制的高2的n次幂位(比如16容量取前4位))
- segment每个锁一个数组,扩容2的n次幂。
- 加了锁后使用头插法不会造成死链 *
- ConcurrentHashMap8是懒汉式初始化
- 容量达到0.75就扩容,不需要超过。
- capacity不是指定容量,而是要放的数量,小于12时,数组长度为16,大于等于12时,数组长度为32。(指定扩容因子为0.75)
- // tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity »> 1) + 1)) = i + i/2 + 1
- // long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor); = i / l + 1
- // int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
- ConcurrentHashMap会将给定的capacity参数与一个阈值进行比较,如果大于阈值,则直接使用阈值;否则,会将capacity转化为大于等于它的最小的2的幂。这样得到的数组大小就是初始数组的大小。
- 注意,具体的阈值和转化过程可能会因版本而异,在1.8的版本中,阈值是1 « 30 ( 2^30=1073741824)
- load factor只在初始计算容量才会按指定数据使用。以后每次扩容时固定为0.75。
- ConcurrentHashMap8把锁加在链表头上。
- 扩容时链表需要重新计算。指针指向改变的节点不能使用同一个节点要重新创建,进而解决并发扩容和查询的问题。put这个链表的线程会阻塞。
- 扩容时每个链表迁移后用forwaindingNode节点代替原有链表。put这个链表的线程会在ConcurrentHashMap8的优化后的扩容区间里进行帮忙链表迁移操作,而不是阻塞。
8. ThreadLocal
要求
- 掌握 ThreadLocal 的作用与原理
- 掌握 ThreadLocal 的内存释放时机
作用
- ThreadLocal 可以实现【资源对象】的线程隔离,让每个线程各用各的【资源对象】,避免争用引发的线程安全问题
- ThreadLocal 同时实现了线程内的资源共享
- ThreadLocal不同线程间隔离,同一个线程共享变量。
原理
每个线程内有一个 ThreadLocalMap 类型的成员变量,用来存储资源对象
- 调用 set 方法,就是以 ThreadLocal 自己作为 key,资源对象作为 value,放入当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 集合中
- 调用 get 方法,就是以 ThreadLocal 自己作为 key,到当前线程中查找关联的资源值
- 调用 remove 方法,就是以 ThreadLocal 自己作为 key,移除当前线程关联的资源值
ThreadLocalMap 的一些特点
- key 的 hash 值统一分配
- 初始容量 16,扩容因子 2/3,扩容容量翻倍
- key 索引冲突后用开放寻址法解决冲突
弱引用 key
ThreadLocalMap 中的 key 被设计为弱引用,原因如下
- Thread 可能需要长时间运行(如线程池中的线程),如果 key 不再使用,需要在内存不足(GC)时释放其占用的内存
内存释放时机
- 被动 GC 释放 key
- 仅是让 key 的内存释放,关联 value 的内存并不会释放
- 懒惰被动释放 value
- get key 时,发现是 null key,则释放其 value 内存
- set key 时,会使用启发式扫描,清除临近的 null key 的 value 内存,启发次数与元素个数,是否发现 null key 有关
- 主动 remove 释放 key,value
- 会同时释放 key,value 的内存,也会清除临近的 null key 的 value 内存
- 推荐使用它,因为一般使用 ThreadLocal 时都把它作为静态变量(即强引用),因此无法被动依靠 GC 回收
记录线程池lambda
public class TestThreadPoolExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger c = new AtomicInteger(1);
// 数组阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
3,
0, // 救急线程的生存时间,生存时间内没有新任务,此线程资源会释放
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queue,
// ThreadFactory 是一个接口,它提供了一个 newThread 方法,用来创建新的线程。 lambda 表达式实际上就是实现了这个方法。
// 其中 new Thread(r, "myThread" + c.getAndIncrement()) 将runnable r作为参数传入,创建了一个新线程并启动了它。
r -> new Thread(r, "myThread" + c.getAndIncrement()),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
Thread thread = new Thread("myThread" + c.getAndIncrement());
// Thread(Runnable target, String name)
// 声明具体接口类型 确定lambda表达式所表示的具体抽象方法
Runnable rr = () -> {};
// 错误的写法,传入的参数Runnable r没有起到任何作用。实现该接口时应该使用方法里的固定的参数(Runnable r)实现约定的抽象方法(返回Thread对象)
ThreadFactory threadFactory1 = r -> new Thread(() -> {},"");
// 同样是错误的
ThreadFactory threadFactory11 = r -> new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println();
}
}, "");
// 正确的写法t2和t22。对于有参数的抽象方法可省略小括号(直接定义参数名r箭头指向->方法体),一行代码返回时可省略大括号{}和里面的return。
ThreadFactory t2 = r -> {System.out.println(true);return new Thread(r, "");};
ThreadFactory t22 = new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(@NotNull Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r ,"");
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread("");
ThreadFactory threadFactory3 = r -> new Thread("");
// Thread(Runnable target, String name) {
Thread t222 = new Thread(() -> {logger1.debug("before waiting"); },"");
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("1", 3600000));
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("2", 3600000));
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("3"));
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("4"));
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("5", 3600000));
showState(queue, threadPool);
threadPool.submit(new MyTask("6"));
showState(queue, threadPool);
}
private static void showState(ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue, ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
List<Object> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (Runnable runnable : queue) {
try {
Field callable = FutureTask.class.getDeclaredField("callable");
callable.setAccessible(true);
Object adapter = callable.get(runnable);
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter");
Field task = clazz.getDeclaredField("task");
task.setAccessible(true);
Object o = task.get(adapter);
tasks.add(o);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
main.debug("pool size: {}, queue: {}", threadPool.getPoolSize(), tasks);
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
private final String name;
private final long duration;
public MyTask(String name) {
this(name, 0);
}
public MyTask(String name, long duration) {
this.name = name;
this.duration = duration;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
LoggerUtils.get("myThread").debug("running..." + this);
Thread.sleep(duration);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTask(" + name + ")";
}
}
}